Producers

A tree and grass is an example of an autotroph aka producer.
All organisms require energy, for growth, maintenance, reproduction, locomotion, etc. Hence, for all organisms there must be: a source of energy, a loss of usable energy.
How is solar energy converted to chemical energy? How does this process influence life as we see it on earth?
The transformations of energy from solar radiation to chemical energy and mechanical energy and finally back to heat are a traditional topic of Ecosystem Ecology.
In every ecosystem, all animals must eat other organisms, or, at the very least, secretions of other organisms, to acquire energy. We can follow a sequence of organisms that feed on each other to create a food chain, or a sequence of organisms that feed on each other.
Since a food chain follows the sequence of organisms that feed on each other, it always starts with an organism that gets its energy from an abiotic source, which is usually light from the sun. An organism that gets its energy from an abiotic source is called a producer also known as a autotroph.
Some examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, and even some bacteria. Autotrophs are important because they are a food source for heterotrophs (consumers).
Did you know that plants not only do they turn carbon dioxide into oxygen, by the process called photosynthesis but they are a good food source for most of the creatures on earth.
How is solar energy converted to chemical energy? How does this process influence life as we see it on earth?
The transformations of energy from solar radiation to chemical energy and mechanical energy and finally back to heat are a traditional topic of Ecosystem Ecology.
In every ecosystem, all animals must eat other organisms, or, at the very least, secretions of other organisms, to acquire energy. We can follow a sequence of organisms that feed on each other to create a food chain, or a sequence of organisms that feed on each other.
Since a food chain follows the sequence of organisms that feed on each other, it always starts with an organism that gets its energy from an abiotic source, which is usually light from the sun. An organism that gets its energy from an abiotic source is called a producer also known as a autotroph.
Some examples of autotrophs include plants, algae, and even some bacteria. Autotrophs are important because they are a food source for heterotrophs (consumers).
Did you know that plants not only do they turn carbon dioxide into oxygen, by the process called photosynthesis but they are a good food source for most of the creatures on earth.
Photosynthesis
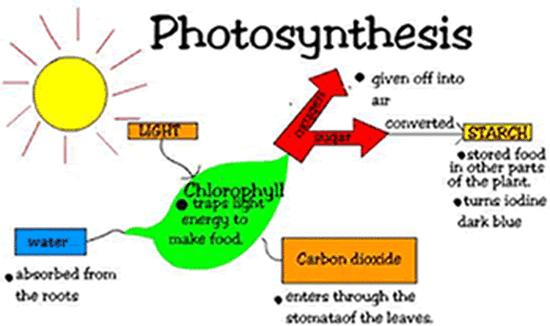
Photosynthesis is the single most important chemical process on earth. It is the process by which plants use solar energy to manufacture food. The term means “putting together with light,” and the process of photosynthesis uses solar energy to form simple sugars from water and carbon dioxide gas. Later these sugars are converted into starch, protein, or fat; and we eat them as fruits and vegetables. Thus photosynthesis changes light energy into food (chemical) energy.
A heterotroph is also called a consumer in the food chain. Consumers are organisms that are unable to produce their own food provisions.They use the food that producers make, or they eat other organisms. Animals are consumers. To stay alive, consumers must get food from other organisms. There are three types of consumers:Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores.
Herbivore

A few examples of herbivores.
An herbivore is an organism that gets its energy from ingesting plants, and only plants.
Carnivore
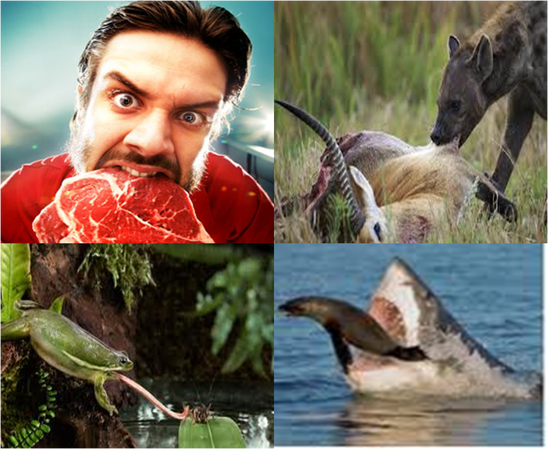

A few examples of carnivores.
A carnivore is an organism that gets its source of energy by hunting and consuming other animals.
Carnivores can feed on other carnivores, omnivores and herbivores.
Carnivores can feed on other carnivores, omnivores and herbivores.
Omnivore

A few examples of omnivores.
Omnivores are considered the "all eaters" they consume both plants and animals for energy.
